
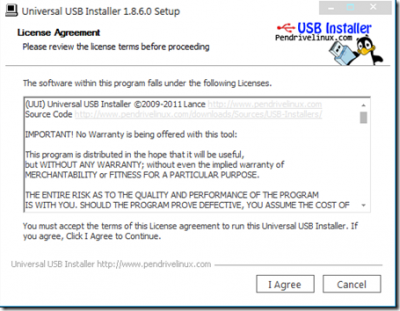
SYSTEMRESCUECD INSTALLER FOR WINDOWS DRIVERS
Hardware, drivers and troubleshooting options ¶ This is because the boot partition is what Grub2 will consider as its root partition during the boot process.
SYSTEMRESCUECD INSTALLER FOR WINDOWS ISO
If you have a separate boot partition mounted on /boot and if you copy this ISO image to /boot/sysrcd/systemrescuecd-x86.iso then the option has to be isoloop=/sysrcd/systemrescuecd-x86.iso. The path of the ISO image may be different from the path on your linux system. This option specifies the path of the ISO image in the partition that grub considers as its root partition.
For that reason, this isoloop=xxx boot option is required in your grub.cfg. When booting an image, SystemRescueCd must be aware that its sysrcd.dat file is in an ISO and not directly on the partition. If you put a copy of systemrescuecd.iso on a partition that Grub2 can read then you can boot SystemRescueCd directly from the ISO image stored on your hard drive.
The default location for a backing-stores file is any file named sysrcd.bs located at the root of a disk which is often a USB stick. If you want to save your backing-store file on a harddisk, boot with backstore=alldev to scan all devices (not just removable devices). To disable the disks scan at boot time specify backstore=off on the boot command line. A backing-store is not mandatory and if the scan fails, it will store the files which have changed in memory. By default, sysresccd automatically scan removable devices (eg: USB sticks) at boot time and uses the first backing-store it finds. A backing-store saves all the changes you can make, so that you keep these changes the next time you boot. backstore=xxx: SystemRescueCd comes with support for the backing-stores.All the actions that are supported by an initscript can be used. Use this option a multiple of times for different services. This does the same thing as /etc/init.d/samba start. For instance if you need the samba service to be started, you can boot with: initscript=samba:start. initscript=service:action: This option allows one to start/stop a service at boot time.Similarly specify a partition using its uuid: root=UUID=b3d3bec5-997a-413e-8449-0d0ec41ccba7. If the label of the partition where linux is installed is mylinux, then boot it using rescuecd root=LABEL=mylinux. So root=auto lets you start the system installed from the CD-ROM in case you have problem with your boot loader or kernel.

The option root=auto will scan all the block devices for a linux system the first linux system found will be started. This option works with LVM volumes, e.g., rescuecd root=/dev/VolGroup00/LogVol00. Keep in mind that you must use a 64bit kernel if your system is made of 64bit programs. For example, if you have linux Gentoo installed on /dev/sda6, use rescuecd root=/dev/sda6 to start it. root=/dev/xdnp: the root= option boots an existing linux system.This way you will not be prompted for the keyboard configuration during the boot. setkmap=kk: defines the keymap to load (example: setkmap=de for German keyboards).Add lowmem if you have less that 400MB of memory of to prevent these directories from being copied. This requires 400MB of memory to cache everything (including the bootdisks and isolinux directories). A slower start but once complete, programs start faster and the CD drive will be released allowing normal access to other CDs. docache: causes the CD-ROM to be fully loaded into memory.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
